How to Import Excel Files in Python
Purpose
Ever struggled to import Excel data into Python for analysis? This post will guide you step-by-step on how to use Pandas to handle Excel files effortlessly, even for complex datasets.
Excel Data Essentials
Excel is a go-to tool for managing and analyzing data. Let’s refresh some key terms to ensure smooth communication:
- Workbook: The entire Excel file.
- Worksheet: Individual sheets (or tabs) within the workbook.
- Header: Labels at the top defining columns (e.g., A, B, C).
- Cells: Data units located at row-column intersections, like A1.
If these terms feel familiar, great! If not, think of them as the building blocks for working with Excel in Python.
Everyday Functionality: Importing Excel Files in Pandas
Real-World Scenario: Metabolomics Data
Imagine you’re analyzing LC/MS metabolomics data from animal samples, with additional metadata. This was my experience at the metabolomics research center, where I worked with a dataset containing:
- Biomarker Assay Worksheet: Measurements for over 100 metabolites.
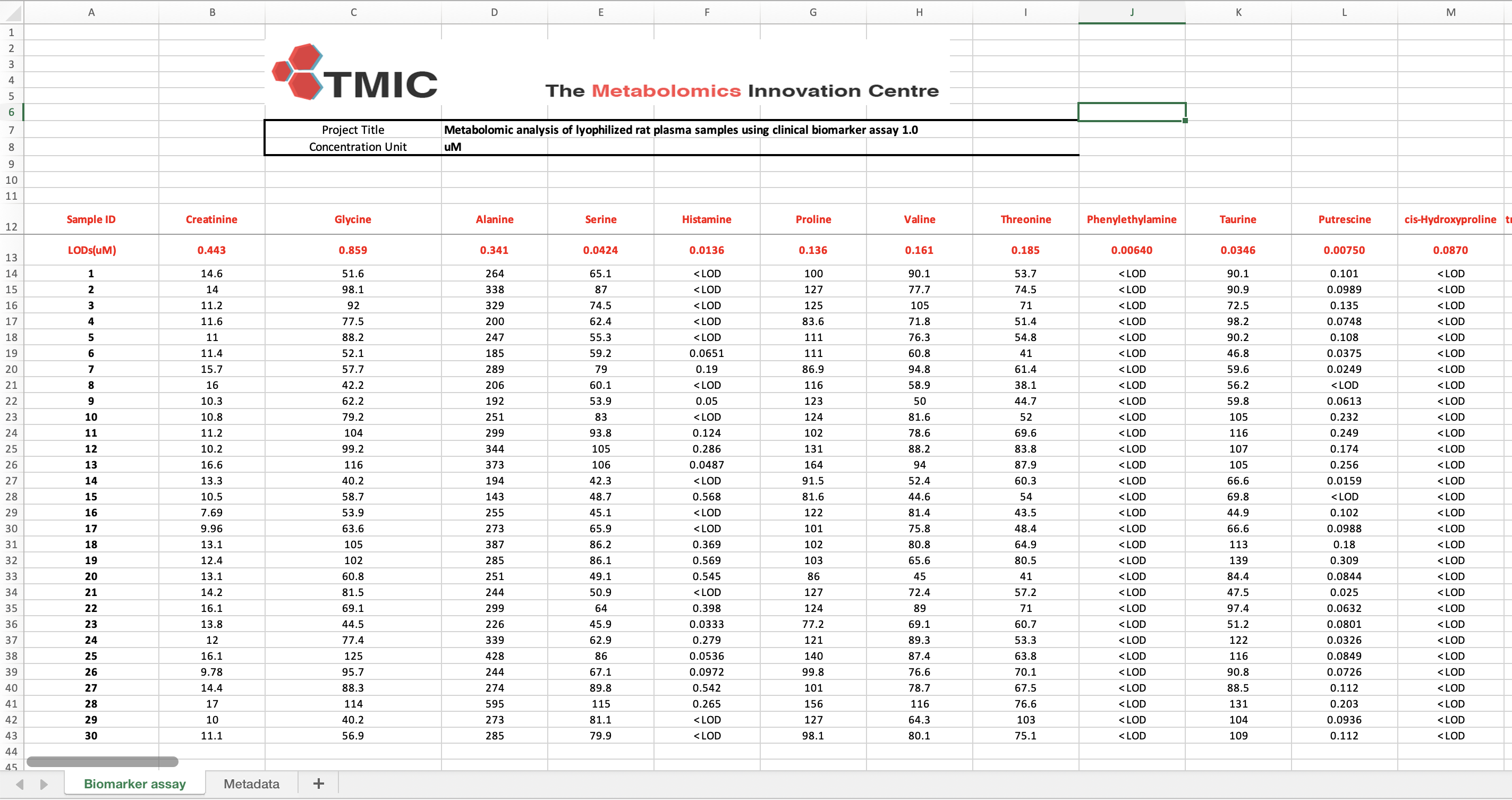
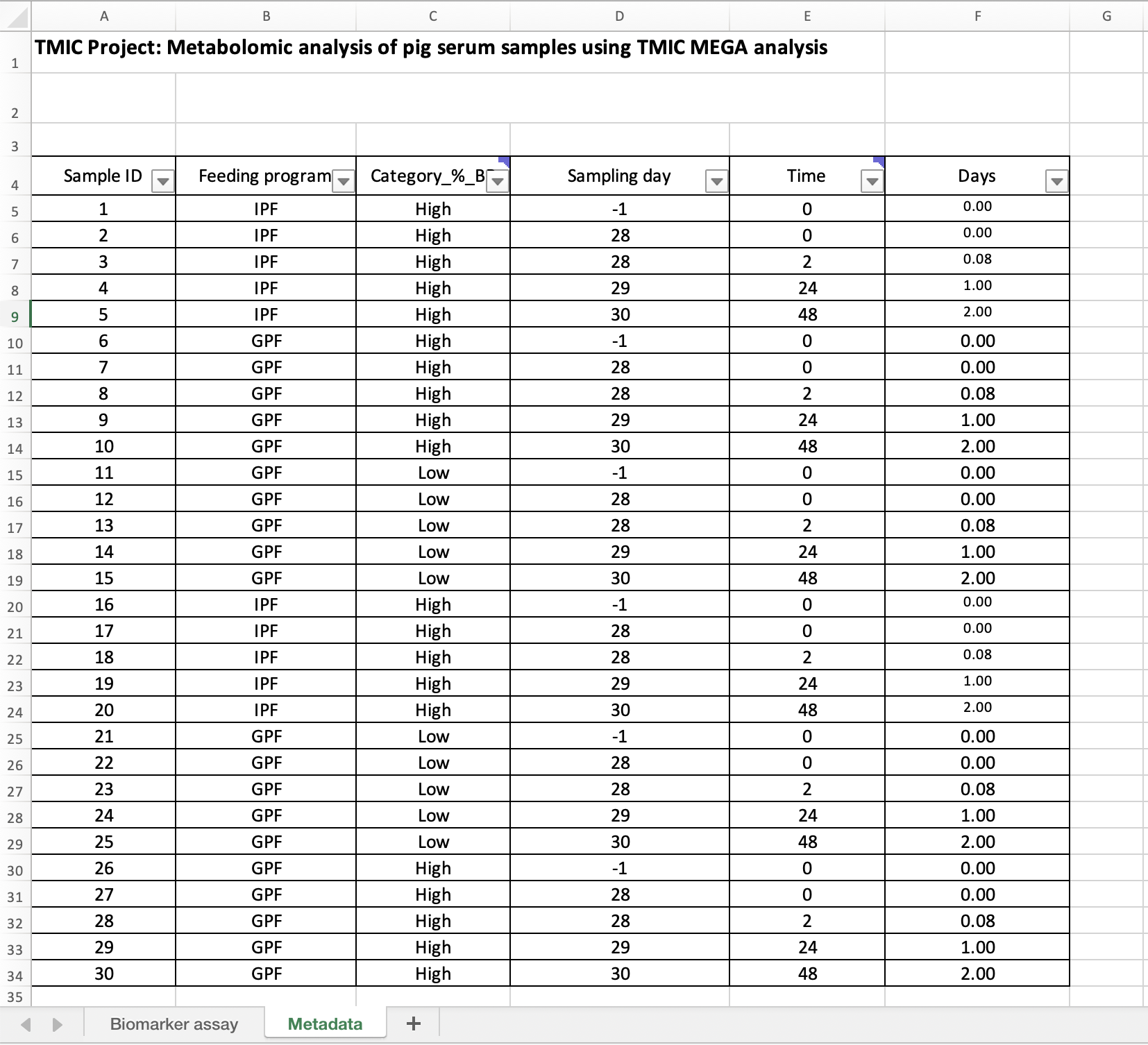
- Metadata Worksheet: Sample information.
Step-by-Step Guide
1. Import Multiple Worksheets
Start by loading a specific worksheet while skipping descriptive rows:
import pandas as pd
df_biomarker_assay = pd.read_excel(
'example-biomarker-assay.xlsx',
sheet_name='Biomarker assay',
skiprows=11
)
>>> df_biomarker_assay.head()
Sample ID Creatinine Glycine Alanine Serine Histamine ... C16:1OH C16OH C18:2 C18:1 C18 C18:1OH
0 LODs(uM) 0.443131 0.859107 0.340909 0.042433 0.013605 ... 0.04906 0.042617 0.058089 0.041081 0.023651 0.056784
1 1 14.600000 51.600000 264.000000 65.100000 < LOD ... < LOD < LOD < LOD < LOD < LOD < LOD
2 2 14.000000 98.100000 338.000000 87.000000 < LOD ... < LOD < LOD < LOD < LOD < LOD < LOD
3 3 11.200000 92.000000 329.000000 74.500000 < LOD ... < LOD < LOD < LOD 0.045089 < LOD < LOD
4 4 11.600000 77.500000 200.000000 62.400000 < LOD ... < LOD < LOD < LOD 0.04134 0.02505 < LOD
[5 rows x 144 columns]
2. Select Specific Rows and Columns
To limit the data to a manageable range:
df_biomarker_assay_selected = pd.read_excel(
'example-biomarker-assay.xlsx',
sheet_name='Biomarker assay',
skiprows=11,
usecols='A:EN',
nrows=31
)
3. Verify Non-Empty Rows and Columns
Check for completeness in the imported data:
nonempty_rows = df_biomarker_assay_selected.dropna(how='all').index.tolist()
count_rows = len(nonempty_rows)
nonempty_cols = df_biomarker_assay_selected.dropna(how='all', axis=1).columns.tolist()
count_cols = len(nonempty_cols)
4. Validate Data Import
Inspect the first and last rows of your dataset to verify that the import matches the source.
Special Use Cases with Pandas
1. Formula-Generated Data
Excel formulas, like those generating the column in the Metadata worksheet, retain their calculated values when imported:
df_metadata = pd.read_excel('example-biomarker-assay.xlsx', sheet_name='Metadata')
2. Filtered Data
Filtered tables (e.g., showing only filtered rows in Excel) are fully imported, including the hidden rows.
3. Binary Workbook Files (.xlsb)
For .xlsb files, use the pyxlsb library to read the data.
Best Practices for Importing Excel Files
To streamline your workflow, follow these tips:
- Use
skiprowsto ignore unnecessary content. - Specify
usecolsandnrowsfor better performance. - Confirm data integrity by checking non-empty rows and columns.
- Choose the correct engine for specialized file formats (e.g.,
.xlsb).
By following these steps, you’ll efficiently prepare your data for analysis, no matter the complexity of the Excel files.
Final Thoughts
Importing Excel files in Python doesn’t have to be daunting. With a clear process, even the most complex datasets become manageable. Try these steps on your own files, and let me know how it goes!
For any questions or advanced use cases, feel free to drop a comment or reach out. Happy coding!